Harsh environments characterized by corrosive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high-intensity friction are considered a "nightmare" for labeling and tagging. These conditions are responsible for numerous challenges, including:
- Surface deformation of labels
- Adhesive layer peeling
- Fading information that becomes difficult to read or scan
- Multiple other critical issues
Corrosive Chemicals: A Major Challenge for Industrial Labels
In industrial and manufacturing settings, labels frequently encounter various corrosive chemical exposures. Below is a guide to chemical classification by severity, highlighting typical examples. Don't hesitate to get in touch with Ricoh directly for a comprehensive consultation for specific chemical interactions not listed here.
| Weak Chemicals | Window Cleaners | Water |
| Moderate Chemicals | Alcohol | Bleach |
| Harsh Chemicals | Gasoline | Oil |
| Extreme Chemicals | Xylene | Acetone |
(According to Zebra - Ricoh's Global Partner in Printing and Barcode Identification Equipment)
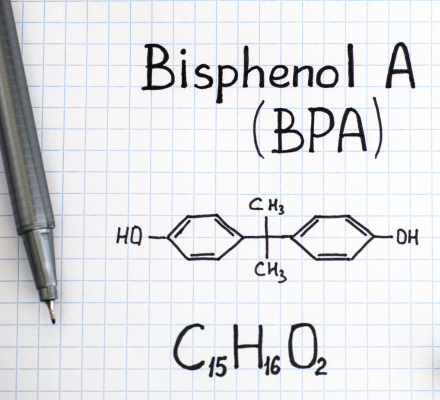
Acetone and Xylene are two characteristic chemicals in harsh environments that cause severe damage to standard labels.
Acetone - a common industrial solvent, has the capability to dissolve standard printing ink, quickly causing label information to blur or disappear completely.
Xylene - a component commonly found in paints, varnishes, and industrial cleaning solutions - not only attacks and fades printing ink but also deforms label surfaces, causing wrinkling, shrinkage, or peeling.
Additionally, other impacts such as high temperatures, exposure to intense light, or high-intensity friction can also contribute to or amplify label degradation. However, within the scope of this article, Ricoh will focus on the most significant destructive factors in harsh environments.
Current Common Methods
Metal Engraving Plates
Advantages
- High durability and excellent resistance
- Long lifespan, up to several decades
Disadvantages
- High production costs
- Difficult to update or customize information when needed
- Not suitable for applications requiring thin, small, high-resolution barcodes

Handwritten Labels
Advantages
- Easy to create, flexible information customization
- No special equipment is required, low-cost
Disadvantages
- Information easily fades or washes away when exposed to chemicals
- Lack of professionalism
- Poor information traceability
- Incompatible with automated management systems
- High human error rate
Thermal Printed Labels with Protective Coating
Advantages
- Ensures long-lasting printed information
- Flexible information customization as needed
Disadvantages
- Requires multiple materials: printing ink, base labels, protective coating
- High costs, long preparation time, complex process
- Difficult to update or customize information when needed
Among the three labeling methods discussed, thermal printing with protective coating offers the most advantages in terms of cost and operations. However, thermal labeling methods still face significant limitations when applied in harsh environments, which will be addressed in the following sections.
Barriers to Thermal Printing in Harsh Environments
Additional Protective Layer Costs
Protective Materials
- Commonly used materials include:
- Polyester (PET) film
- Polypropylene (PP) film
- Vinyl (PVC) Overlaminates
- Fluoropolymers (PTFE, FEP)
- Special coatings like Epoxy, Ceramic, or Silicon coatings
Coating Methods
- Requires specialized machinery for large-scale label lamination
- Manual protection coating requires additional materials and resources
Label Material Durability Challenges
Chemical Exposure Damage
Acids, alkalis, and organic solvents can destroy the molecular structure of label materials, causing decomposition or loss of binding capabilities.
High Temperature Deformation
When exposed to temperatures above 80°C, standard labels can:
- Shrink
- Warp
- Potentially burn, rendering information unreadable
Ink Resistance Limitations
Industrial Solvent Interaction
Solvents like acetone, toluene, and xylene used in manufacturing processes can dissolve standard ink within minutes of contact.
Thermal Durability Degradation
Harsh environments involve frequent thermal impacts. Continuous hot-cold cycles cause expansion and contraction, leading to ink cracking and peeling over time.
Adhesive Layer Neutralization
Acid and Alkaline Reactions
High or low-pH environments can break down adhesive molecular structures, reducing adhesion strength. Many applications require additional tape or nailing to support label adhesion.
Temperature Variations
Extreme high or low temperatures, or significant temperature ranges, can cause label structure contraction, indirectly damaging the adhesive layer.

Ricoh's Solution
As a specialist in label solution providers in Vietnam, Ricoh consistently develops recommendations based on the actual operating environment of labels.
For applications in harsh environments, especially those involving extremely strong chemicals, Ricoh offers customers a solution using Resin B110CU thermal transfer ribbon and corresponding RFR labels.
Why Do the RFR and B110CU Combination Suit Harsh Environments?
Extreme Chemical Resistance
RFR labels are manufactured from high-grade PP & PET materials with an advanced high-tech coating developed and researched by Ricoh. This coating enables resistance against multiple corrosive chemicals. When combined with B110CU thermal transfer ribbon, this duo has successfully passed Ricoh's rigorous chemical resistance tests, including:
Extreme Chemicals: Acetone, Xylene, IPA, Toluene (Tested with 250 friction cycles in solution)
Common Solvents: Machine oil, Lubricants, Ethanol, Thinner (Tested with 250 friction cycles)
The ANSI scale image below further confirms the chemical resistance when combining Resin B110CR thermal transfer ribbon and RFR labels, with all measurements achieving a perfect 5/5 rating.

Superior Printing Quality
The B110CU thermal transfer ribbon is specifically designed to create sharp, high-resolution images on RFR label surfaces.

Additional Physical Impact Resistance
- Withstands temperatures up to 250°C
- Unaffected by continuous 24-hour water immersion
- Resistant to 650W/m² Xenon light exposure
- Endures 50 abrasions with a 1kg hardboard at 100°C
Multiple Label Base Options
- RFR-W: White, Polypropylene
- RFR-WP: White, PET
- RFR-SP: Silver, PET
International Certifications
The Resin B110CU thermal transfer ribbon and RFR labels have achieved critical certifications, including:
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet), RoHS Compliance, Halogen-Free Certification
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): A mandatory certification in many heavy industries: Customers can verify information on the UL website
Benefits of Using B110CU and RFR
Cost Savings: High durability means fewer label replacements, significantly reducing material costs.
Customized Label Printing: Leveraging flexibility, durability, and customization options (size, design, pre-printed information) simultaneously becomes a key advantage.
Reliable Material Sourcing: Customers can order genuine B110CU and RFR labels directly from Ricoh IMS Vietnam, ensuring optimal waiting times and quality.
Applications
Designed specifically for harsh environments with extreme chemical resistance, labels printed with Resin B110CU and RFR are ideal for:
Healthcare: Epidemiological sample labels, Bottle and laboratory equipment labels

Chemical Industry: Chemical drum labels

Transportation Equipment: Component labels, Process management labels

Electronics: PCB circuit labels, Device identification labels

Experiencing Label Issues in Harsh Environments?
Are your current labels struggling to withstand challenging industrial conditions?
Contact Ricoh immediately for expert consultation and free samples!

Let’s connect
Get in touch with one of our consultants and find out how we can help you to implement a barcode system
Recommended resources for you
.png)
Things You Should Know About Warehouse Management in 2024
Discover the top trend of warehouse management in 2024

Direct Thermal or Thermal Transfer: Which One To Choose?
This article will provide step-by-step guidance to help you navigate the world of thermal printing technology.