Common Cold Storage Environments and Their Specific Requirements
According to Vietnam Briefing, cold storage facilities are categorized as follows:
| Type | Temperature |
| Cryogenic Storage | -40°C - 10°C |
| Refrigerated Storage | -5°C - 10°C |
| Cooling Storage | 3°C - 15°C |
Regarding common cold temperature ranges in industries:
- According to HACCP standards, the safe temperature zone for food is below 5°C.
- The Australian Food Safety Information Association recommends storing food at temperatures from -15°C to 5°C, or lower for long-term storage.
- The FDA suggests temperatures from -25°C to -15°C for storing vaccines, biological products, or medical test samples.
- Long-term food storage temperature of -22°C to -18°C is recommended by experts.
Generally, the temperature range from -25°C to 5°C is widely applied across many fields, especially in food, biotechnology, and healthcare. This is the temperature range businesses need to consider when choosing an appropriate labeling solution.
However, freezing temperatures are "enemies" of thermal labels, posing significant challenges to the process of labeling and preserving product information. Direct thermal labels are typically used in temperature conditions of -4°C or above when applying labels.
- Operating temperature range of labels: -54°C to 90°C
- Label application temperature: -4°C or above
- Service temperature range: -54°C to 93°C

Besides temperature, humidity is another important parameter to consider. Typically, humidity in cold storage needs to be maintained between 60% and 90%, depending on the type of product being stored.
Negative Effects of Freezing Temperatures on Conventional Labels
Traditional labels are not designed to withstand low-temperature conditions, so when placed in freezing environments, they often encounter the following issues:
Surface Deformation
Low temperatures cause the label material to shrink, become brittle, and easily tear, reducing longevity and failing to maintain its original shape.
Loss of Adhesion
The adhesive layer loses adhesion due to freezing or moisture on the application surface, making the label prone to peeling and slipping off the product.
Information Blurring
Low-temperature environments break the bonds of molecules constituting the ink, reducing durability. High humidity will wash away ink particles, causing information to blur or fade. This leads to difficulty reading information with the naked eye or scanning devices.
Effects of Plasticizers
Plasticizers from packaging, when stacked together, can penetrate the ink surface, information layer, and adhesive layer. Low temperatures break bonds, reducing ink and adhesive bonding, which are then pulled out by plasticizers, damaging the label.
Potential Damages of Using Inappropriate Labels
Three main types of damage can occur:

150LCS-B W2-CL2: Optimal Solution for Freezing Environments
To address these challenges, Ricoh has developed the 150LCS-B W2-CL2 label solution - a specialized product designed specifically for freezing environments.
Why 150LCS-B W2-CL2 is Suitable for Freezing Environments
Advanced Adhesive Technology
Water-based Acrylic adhesive that's safe and specially designed for freezing with an adhesive strength of at least 6N/25mm while having high load-bearing capacity up to 10,000 seconds under 1kg load at 40°C.
See more detailed specifications
The operating temperature range of the adhesive layer is optimized between -20°C and 35°C.
Suitable Label Surface
150LCS-B W2-CL2 is developed based on film material, providing high water resistance and tear resistance, which is crucial when freezing environments come with moisture and water in addition to low temperatures.
Meeting International Standards
Direct thermal label 150LCS-B W2-CL2 meets international safety standards.
Contact us now for more details.

Factors That Make 150LCS-B W2-CL2 Outstanding
Durable Resistance
Ricoh's direct thermal paper surface is composed of 5 special chemical layers, creating superior quality, enhancing resistance properties, and protecting thermal images.
Below is an overview of the layers of Ricoh thermal paper and their roles. (Note: These layers do not include the adhesive layer and silicone base layer)
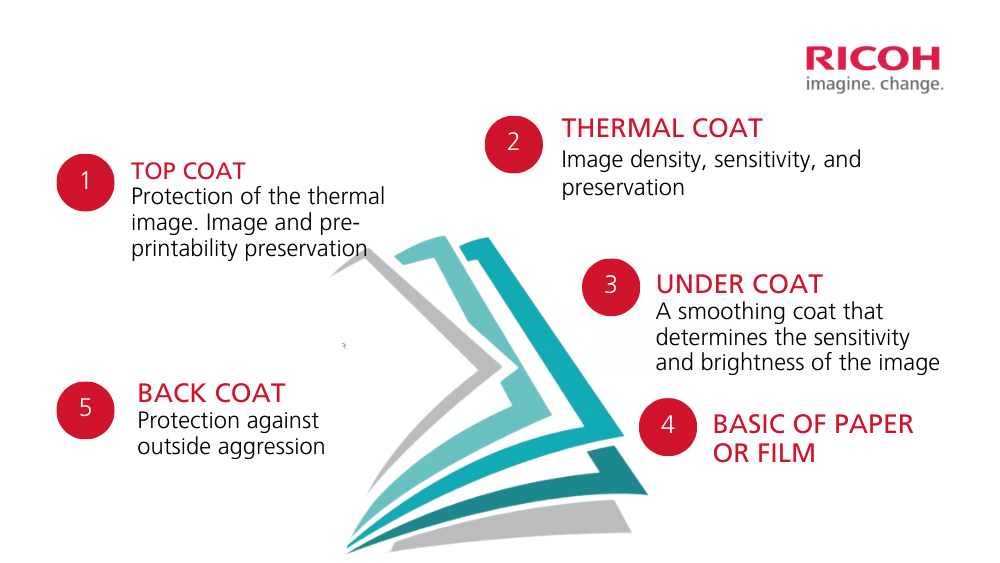
Additionally, with this 5-layer structure, the direct thermal label 150LCS-B W2-CL2 is always friendly to the thermal printer's printhead and reduces static electricity.
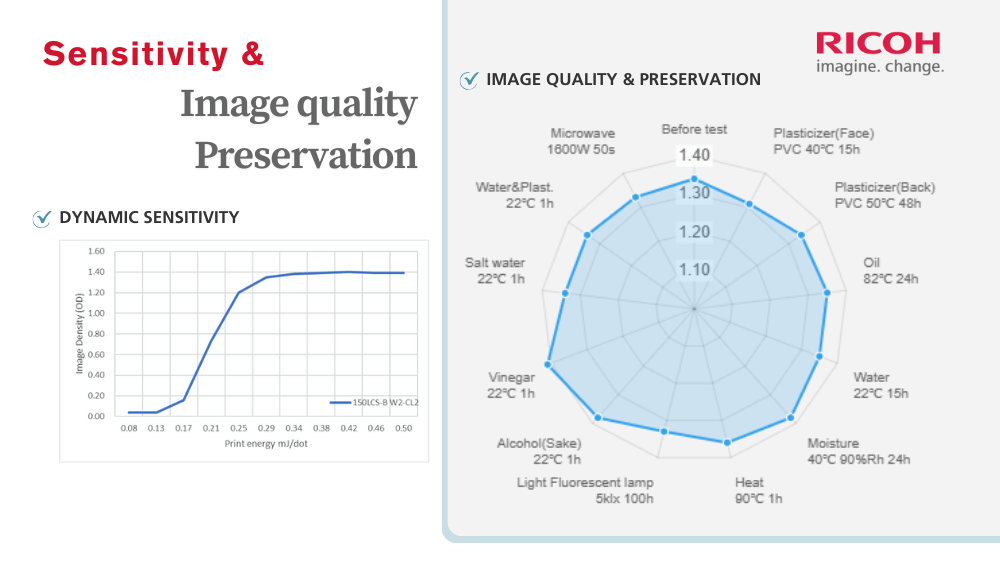
High-Quality Images
Thanks to the 5-layer surface structure, images printed by 150LCS-B W2-CL2 can resist impacts as shown below. Contact Ricoh now for more advice.
Friendly to Barcode Printer Printheads
The printer's printhead only needs to be set at a lower temperature level compared to regular labels, thanks to the high thermal sensitivity index of 150LCS-B W2-CL2. Lower printhead temperature will prevent the printhead from maintaining high temperatures continuously and deactivating the printhead heating resistor.
Applications
With its outstanding characteristics, 150LCS-B W2-CL2 labels can be widely applied in many fields:
Food Industry
- Specific applications: Labeling for frozen meat, seafood, vegetables, post-processing food industry requiring cold storage, and food during the thawing process
- Conditions: Cool storage environments (3°C - 15°C) and freezing (-5°C to -20°C), thawing process (<7°C)
Read more now, All you need to know about Food label

Pharmaceutical Industry
- Specific applications: Labeling vaccines, cold-stored medications, serums, pathological samples, medical biologicals, biological preparations, blood, and blood components
- Conditions: Standard cold storage environments (2°C - 8°C), special frozen storage (-15°C to -20°C), medical cold rooms with strictly controlled temperatures
Read more about Apply Barcode to Pharmaceuticals
Logistics and Cold Supply Chain
- Specific applications: Labeling frozen shipments, cold containers, frozen pallets, insulated styrofoam boxes, dry ice bags, temperature monitoring labels
- Conditions: Exposure to temperature fluctuations during transportation (-20°C to 35°C), high humidity environments, freeze-thaw-freeze cycles during transportation, exposure to ice and dry ice

Other Industries
- Specific applications: Labeling cold chemicals, frozen biological samples, temperature-sensitive electronic components, laboratory samples, semiconductor materials, water and soil analysis samples
- Conditions: Cold laboratory environments (-20°C to 5°C), special industrial refrigerators, exposure to chemicals in low-temperature conditions, research environments with controlled humidity
Advantages of the Direct Thermal Printing Method
High Convenience
Direct thermal printing doesn't require ink ribbons, saving costs on management, storage, and replacement time, while minimizing the risk of production interruptions due to lack of consumables.
How direct thermal labels work:
Ensured Safety
Direct thermal label contains no harmful substances, ensuring safety for food and users, particularly important for products in direct contact with food or pharmaceuticals.
High Information Security
The direct thermal printing method leaves no waste products, unlike when using thermal transfer ribbons (TTR), important for industries requiring high security, such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, or biotechnology.
Fast Printing Speed
Direct thermal technology allows high-speed printing, increasing the efficiency of production and packaging processes, an advantage for large-scale manufacturing businesses, especially in the food and logistics industries.
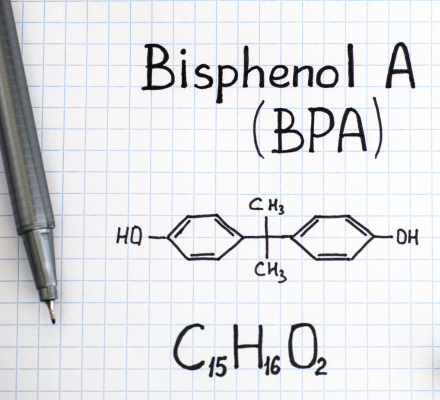
Sustainability
150LCS-B W2-CL2 labels meet standards for being BPA and Phenol-free, ensuring user safety and environmental friendliness.
Experiencing Label Issues in Freezing Environments?
Contact Ricoh Vietnam today for a detailed consultation on 150LCS-B W2-CL2 label solutions and how to effectively apply them to your business operations.

Let’s connect
Get in touch with one of our consultants and find out how we can help you to implement a barcode system
Recommended resources for you
.png)
Things You Should Know About Warehouse Management in 2024
Discover the top trend of warehouse management in 2024

Direct Thermal or Thermal Transfer: Which One To Choose?
This article will provide step-by-step guidance to help you navigate the world of thermal printing technology.