Barriers to choosing label solutions for electronics
Labels that don't meet electrostatic regulations
ESD stands for Electrostatic Discharge, meaning the discharge of static electricity, a static charge created when two surfaces come into contact and then separate, with at least one of these surfaces having high resistivity.
In Electronics, static electricity can occur during the self-adhesive labeling process. If the labels don't have sufficient anti-static capabilities, there's a risk of signal interference, explosions, and serious damage to the surface of the labeled device.
Print quality and image clarity are insufficient
In electronics, labels are often applied to surfaces with small areas such as Printed Circuit Boards (PCB). This creates a "dual standard" where labels need to be small enough while still clearly displaying information including barcodes, serial numbers, etc.
However, when printing characters and barcodes on small-sized label backgrounds, businesses need to equip themselves with high-resolution printers along with thermal transfer ribbons compatible with the printer's specifications. If either of these conditions is not met, labels may appear blurry or cracked, making it difficult for common scanners to read the data.
To ensure sharpness, electronics often use TTR compatible with printers that have 600 dpi print heads. Read more about Barcode printer resolution (DPI) in our related article.
Labels damaged due to harsh external factors
During operation, labels are frequently exposed to high temperatures, chemicals, and solvent vapors. This causes labels to deteriorate, peel off, and the TTR to corrode or fade. Information on the labels becomes unrecognizable by scanners or the naked eye, causing difficulties in identification and delays in the production process.
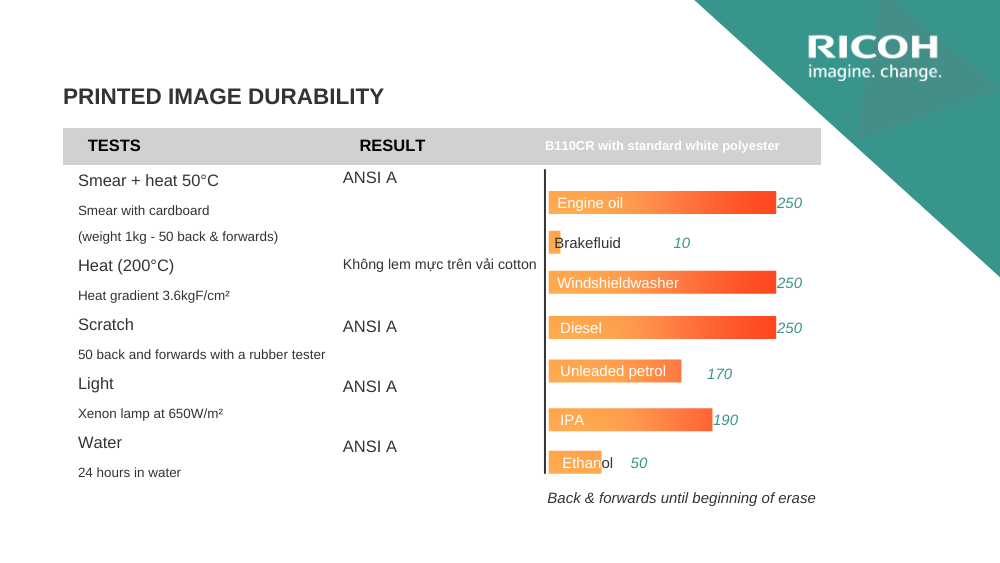
For example, a recent Ricoh customer specializing in motor manufacturing encountered a major issue in their production line. After the devices went through a 90°C drying process in an industrial drying chamber, information couldn't be retrieved for the assembly step because the images had become blurred due to TTR melting. Let's follow Ricoh's solution at the end of this article.

International safety standards and certifications
The electronics industry must comply with numerous standards such as RoHS, REACH, and UL related to safety and the environment. Labels play a role as a component of the final product, so the materials used to create labels also need to meet these standards.
4 reasons why B110CR is the optimal choice for Electronics
B110CR meets electrostatic requirements
B110CR is a Resin type that has achieved UL certification for electrostatic properties. Customers can refer to the following two standards:
- UL 746C - Safety Standard for Polymeric Materials - Use in Electrical Equipment Evaluations, which specifies requirements for electrostatic resistance for plastic materials such as labels.
- UL 60950 - Safety Standard for Information Technology Equipment, which sets requirements for anti-static materials and static discharge resistance for equipment.
Customers can look up compatible labels at the following UL page link: B110CR Product Matching
B110CR produces sharp images with high resolution after printing
In a recent test, labels made from coated film material printed with B110CR thermal transfer ribbon demonstrated the ability to print small characters and components while ensuring readability by Zebra handheld scanners and Keyence specialized barcode verifiers.
Check it out: the test barcode in this sample is small and measures 8x8mm
(In case you can not watch the video on site, access this link)
Below is a description of the image quality of the B110CR when printing on synthetic materials:

B110CR withstands temperatures up to 200°C & has superior chemical resistance
The following table shows temperatures recorded on some components (as reported by some of Ricoh's customers) in the Electronics:
| Devices | Temperature |
Microprocessor ICs | 70°C – 100°C |
| High-efficiency PCB | 80°C – 120°C |
| Power supply | 80°C – 120°C |
| CPU (Central Processing Unit) | 66°C – 105°C |
Receive the B110CR datasheet here:
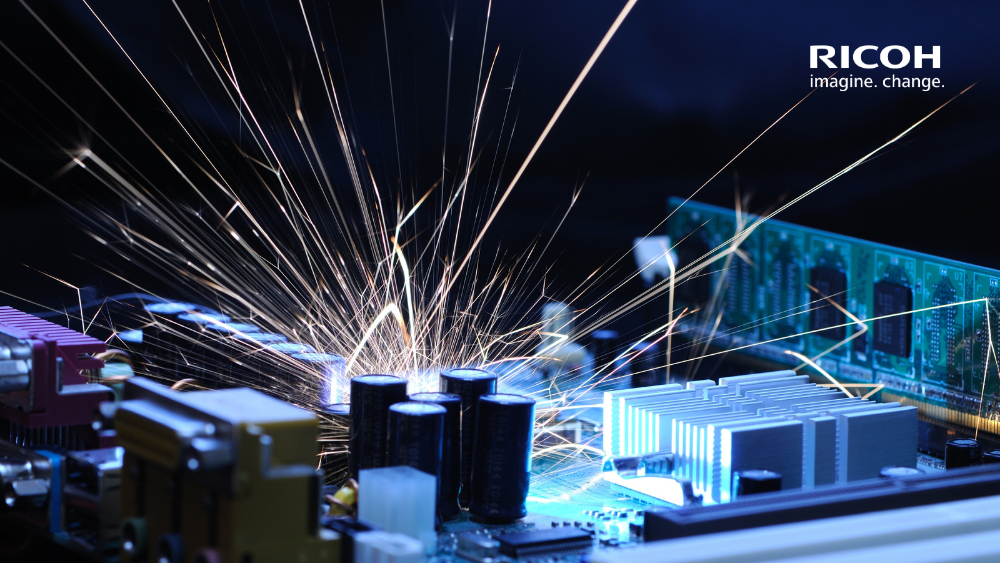
B110CR can resist impacts from chemicals, gasoline, oils, alcohol, and concentrated solutions. Moreover, it offers superior scratch resistance against high-intensity friction.

Below is a chart showing the resistance parameters to external agents for labels printed with B110CR:
B110CR meets international safety standards and certifications
B110CR has achieved many certifications such as RoHS, REACH, UL, MSDS, HALOGEN FREE, PFOS/PFOA, 6P, and MOSH/MOAH.
| Certificate | Stand for | Details |
| RoHS | Restriction of Hazardous Substances | Certification that products sold in Europe comply with regulations on hazardous substances such as Pb, Hg, Cd, Cr6+, PBB, and PBDE |
| REACH | Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals | Certification that the product meets regulations for about 200 chemicals according to EU standards |
| UL | Underwriters Laboratories | Certification ensures that products sold in North America meet UL safety standards |
| MSDS | Material Safety Data Sheet | A data document containing information to ensure safety for those who come into contact with or work with the material |
| HF | Halogen Free | Certification that the product complies with regulations on Halogen compounds such as Br, Cr, F |
| PFOS/PFOA | Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Perfluorooctanoic Acid | Certification that the product complies with regulations on Perfluorinated compounds (PFOS, PFOA) |
| 6P | Six Principles | Certification that the product complies with 6 safety and hygiene principles issued by the US FDA, including Prevention, Operating Principle, Risk Assessment, Compliance, Change Management, and External Audit |
| MOSH/MOAH | Mineral Oil Saturated/ Aromatic Hydrocarbon | Safety certification for products ensures regulations on mineral oil compounds |
If businesses need to view certification information, don't hesitate to contact Ricoh IMS Vietnam directly via email at [email protected].Ricoh also has a policy to support customers in registering for inspection according to the standards of other certifications.

Success Case
Challenge
As previously shared, Ricoh's customer required labels that could withstand temperatures in industrial drying ovens when applied to motors.
Before contacting Ricoh, the customer was using an unbranded Wax Resin ribbon. Consequently, when printing and testing the drying process, the images produced by this TTR became blurred due to TTR melting, leading to barcode scanners being unable to read the encoded data.
The label material is used:
Material: Coated film
Dimensions:
- Box label: 120 x 50 mm
- Circuit board label: 50 x 20 mm
Export markets: Taiwan and Canada
Additionally, not knowing the brand of the product prevented the customer from researching to propose another TTR type with higher resistance, such as Resin ribbon.
Proposed Solution
Understanding the customer's requirement for a thermal transfer ribbon capable of withstanding temperatures above 90°C - 120°C, Ricoh's consultant proposed two product codes: B120EC and B110CR.
Regarding B120EC, this Resin roll is specialized for use with both flat and near-edge printheads. Its resistance capabilities include:
- Heat resistance up to 150°C
- Resistance to oils, alcohol, gasoline
- Compatible with many synthetic materials such as PET/PP/PE/PVC
- Achieved certifications such as RoHS, REACH, UL, WEEE, MSDS, HALOGEN FREE, PFOS/PFOA, 6P
Results Achieved
Both of these TTR codes met the requirements for image quality and heat resistance.The images printed on labels after going through the drying oven no longer smudged and completely resolved the TTR melting issue.
Ready to use B110CR to print your electronic labels?
Get in touch with one of our consultants and get B110CR sample rolls or consultation
Let's Connect
Let’s connect
Get in touch with one of our consultants and find out how we can help you to implement a barcode system
Recommended resources for you
.png)
Things You Should Know About Warehouse Management in 2024
Discover the top trend of warehouse management in 2024

Direct Thermal or Thermal Transfer: Which One To Choose?
This article will provide step-by-step guidance to help you navigate the world of thermal printing technology.